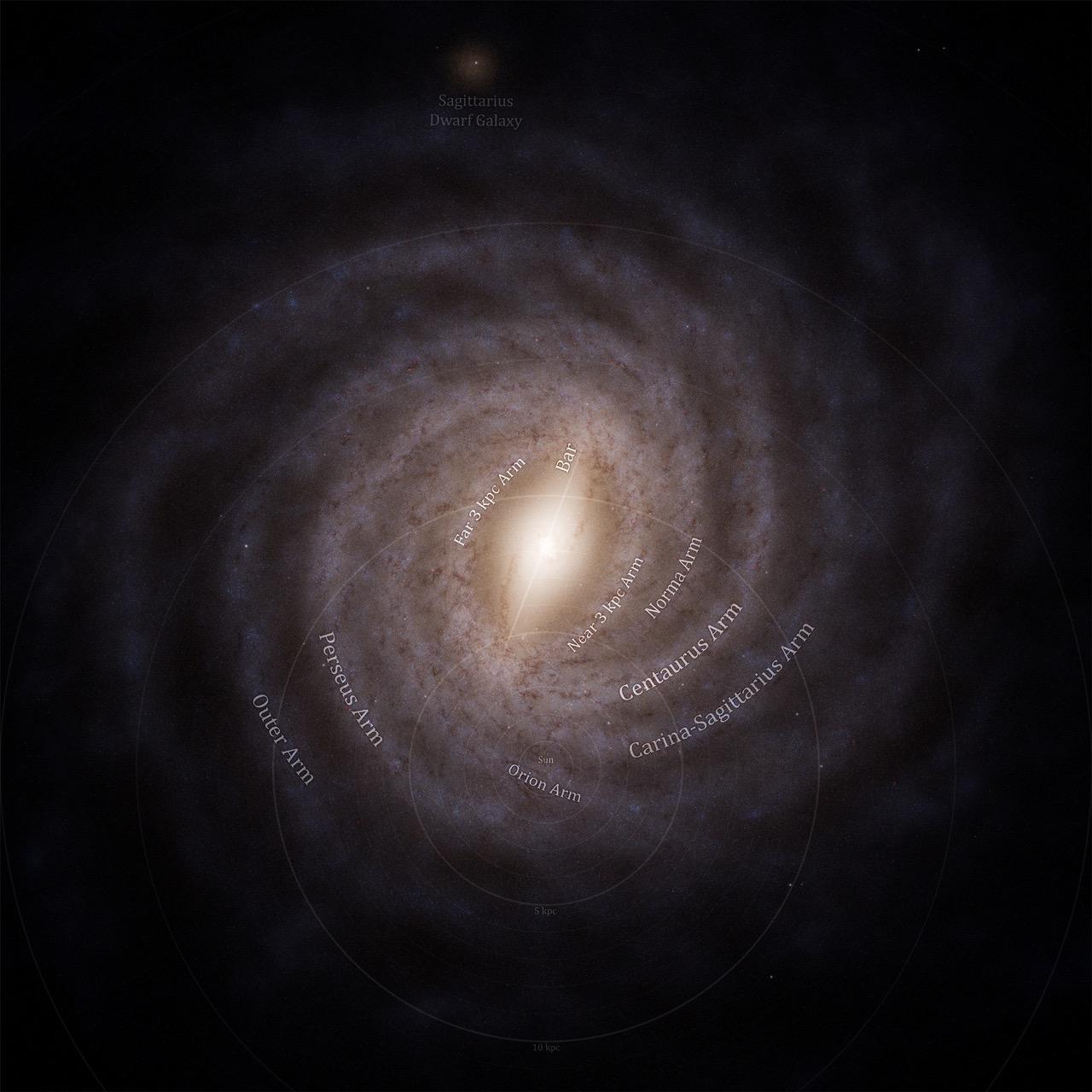
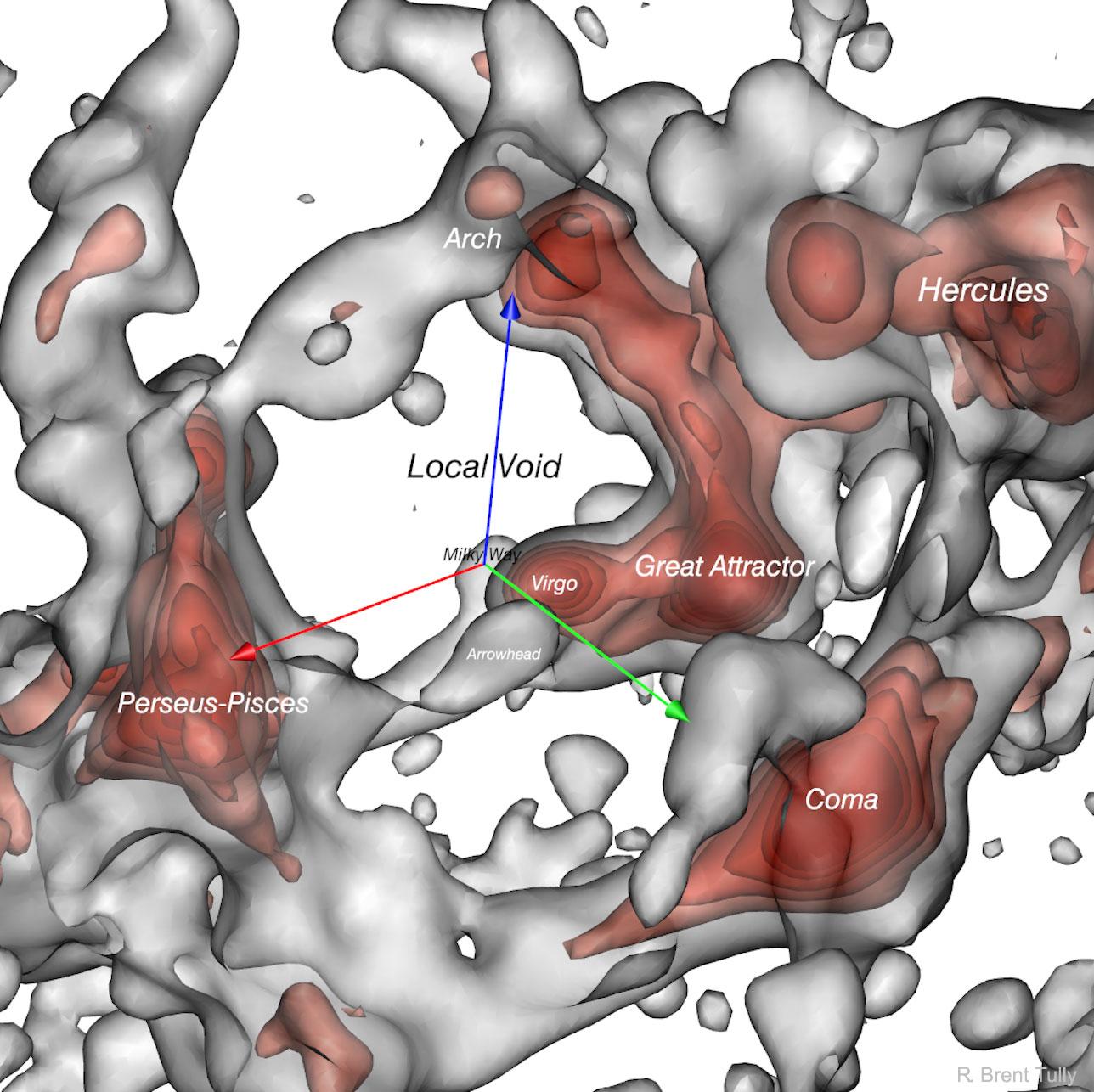
a cosmographic map featuring the cosmological large scale structure in our local cosmic neighborhood. The density field is displayed as semi-transparent isosurfaces, colored grey for the the lower isocontour value, and colored in nuances of red for five higher levels. The resulting structure is filamentary, with high-density knots at the filaments' crossing, an architecture typical of the Cosmic Web. Three colored arrows materialize the cardinal axes of the Supergalactic Coordiante System, centered at our location. Several important actors of our local cosmography are named: Milky Way, Virgo, Arrowhead, Great Attractor, Perseus-Pisces, Coma, Arch, Hercules. The name of the astronomer leading the study is inprinted in the lower right corner of the figure, reading R. Brent Tully. All these elements are drawn against a white background.